Is your PC warning you about a “CPU Fan Speed Detection Error”?
It’s a message no one wants to see especially mid game or during important work. When your system throws this error, it’s signaling a potentially serious issue: your CPU fan may not be operating correctly.
This isn’t just an annoying pop up it’s a critical alert. Your CPU relies on proper cooling to maintain safe operating temperatures. If the fan isn’t spinning or being detected, your processor could overheat, leading to sudden shutdowns, sluggish performance, or even long term damage.
Why does this happen, and more importantly, how can you fix it?
Resolving CPU Fan Speed Detection Errors: A Comprehensive Guide
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know, including:
- What causes the CPU fan speed detection error
- How to diagnose and fix it step by step
- Prevention tips to keep your system cool and error free
Whether you’re a casual PC user or a seasoned technician, this guide has actionable insights tailored to your experience level.

Let’s get started.
What Is the CPU Fan Speed Detection Error?
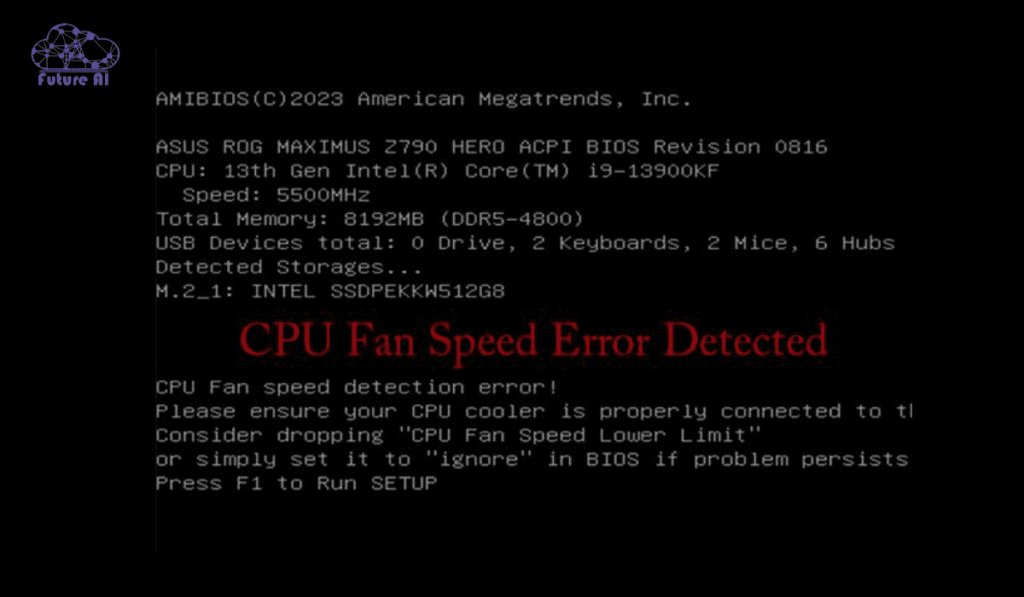
The CPU fan speed detection error is a BIOS or system or level alert indicating that your motherboard cannot detect or properly read the RPM (revolutions per minute) of your CPU’s cooling fan. This error typically appears during startup, often accompanied by a warning like:
“CPU Fan Error! Press F1 to Resume” or “CPU Fan Speed N/A.”
Ignoring this message can be risky. If the CPU fan truly isn’t spinning or isn’t detected, the CPU can quickly overheat leading to thermal throttling, system crashes, or permanent damage.
Want to prevent CPU errors before they start?
👉 Check out our step-by-step guide on How to Clean Your CPU and keep your system running cool and error-free. It's the perfect companion to understanding and fixing CPU Fan Speed Detection Errors.
Common Causes of CPU Fan Speed Detection Errors
Understanding the root cause is the first step to fixing the issue. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Hardware Issues
- Dust Accumulation: Dust buildup in the heatsink or fan can cause the fan to stop spinning or run erratically, triggering detection failures.
- Loose or Disconnected Cables: If the CPU fan cable is not properly seated in the CPU FAN header, the motherboard can’t monitor its RPM.
- Faulty Fan or Motherboard Header: A damaged fan or a non-functional fan header can prevent RPM data from being transmitted to the BIOS.
2. Software or BIOS Configuration Issues
- Incorrect BIOS Settings: Fan monitoring might be disabled or incorrectly configured in the BIOS. Some motherboards require minimum fan RPM thresholds, and silent/low RPM fans might not meet that threshold.
- Outdated Firmware or BIOS: Bugs in outdated BIOS versions can cause false fan error warnings, even if the fan is functioning properly.
3. User Induced Factors
- Overclocking: Increased thermal output from overclocking can exceed the fan’s cooling capabilities, triggering alerts even when the fan is spinning.
- Improper Fan Installation: Installing the fan in the wrong header (e.g., SYS FAN instead of CPU FAN) or not securing it tightly to the CPU can lead to detection issues or overheating.
Experiencing fan speed errors?
Don’t guess—monitor your CPU’s temperature the right way.
👉 Check out our guide on How to Check CPU Temperature in Windows 10 using easy methods and trusted tools.
Diagnosing the CPU Fan Speed Detection Error
Before you can fix a CPU fan speed detection error, you need to correctly diagnose the root cause. This section walks you through a clear step by step process using both physical inspection and software diagnostics perfect for both beginners and seasoned users.
Initial Checks: The Physical Inspection
Start with the basics before diving into BIOS or software tools:
- Observe the Fan at Boot: Open your case (safely) and check if the CPU fan spins when you power on the PC. If it doesn’t spin, the issue is likely hardware related.
- Check Fan Connection: Ensure the fan is securely connected to the correct header CPU_FAN, not CHA_FAN or SYS_FAN.
- Inspect the Wires and Header: Look for bent pins, frayed cables, or disconnected wires that may prevent proper signal transmission.
Pro Tip: Refer to your motherboard manual to confirm the exact location of the CPU FAN header.
BIOS Inspection: Is Your Fan Recognized?
If the fan physically spins, but you’re still seeing errors, the next step is your BIOS.
- Enter BIOS/UEFI Setup: Restart your PC and press the appropriate key (usually DEL, F2, or ESC) during startup.
- Navigate to Hardware Monitoring Section: Look for menus like “Monitor”, “Fan Settings”, or “PC Health Status.”
- Check Fan Status: See if the CPU fan is being detected and whether an RPM value is displayed.
- Adjust Fan Thresholds: If your fan runs quietly or has low RPM, you may need to lower the minimum RPM threshold to prevent false alarms.
- Enable Smart Fan Settings: On some motherboards, enabling “Smart Fan” or “Q Fan Control” allows better RPM scaling and monitoring.
Use Software Tools for Monitoring
If the BIOS confirms fan detection, but you’re still getting errors, software based diagnostics can help verify fan behavior over time.
Top Recommended Tools:
- HWMonitor – Displays live fan speeds, voltages, and CPU temps.
- SpeedFan – Allows fine tuned fan control and temperature based profiles.
- Open Hardware Monitor – Offers a visual breakdown of sensor data and RPM trends.
✅ These tools can help confirm whether your CPU fan is fluctuating, running too slow, or not being reported accurately by the system.
Step by Step Troubleshooting Guide
Once you’ve diagnosed the issue, it’s time to walk through a structured troubleshooting process to resolve the CPU fan speed detection error. These actionable steps address both hardware and software related causes perfect for DIY users and professionals alike.
1. Cleaning and Maintenance
Dust buildup can block fan movement or interfere with sensor accuracy. Regular cleaning helps restore proper fan function.
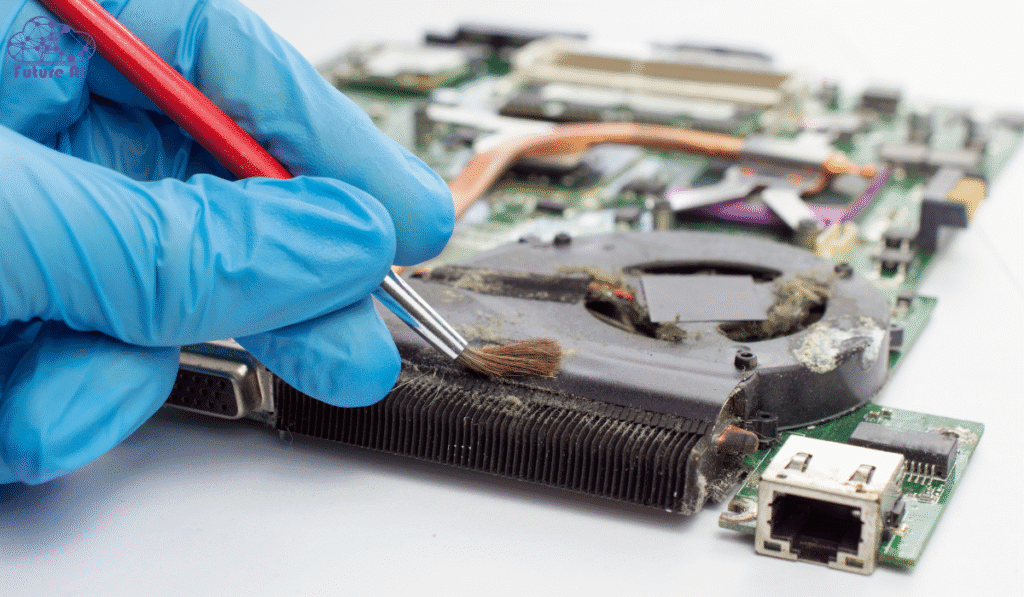
- Shut Down and Unplug Your PC: Always power off and disconnect from electricity before opening the case.
- Remove Dust Safely: Use compressed air to blow dust out of the CPU fan, heatsink, and case vents. Avoid using cloths or vacuum cleaners that may create static discharge.
- Ensure Unobstructed Airflow: Make sure no cables or objects are blocking the fan blades or airflow paths.
Tip: Clean your PC every 3 to 6 months, especially in dusty environments.
2. Checking Connections
A loose or misplaced connection is one of the most common causes of this error.
- Verify the Fan Connector: Ensure the fan’s 3 or 4 pin connector is securely inserted into the CPU_FAN header on the motherboard not a chassis or system fan header.
- Test with a Different Header or System: Move the CPU fan to a different fan header (if available) or try connecting it to another motherboard to confirm whether the fan or the header is faulty.
- Inspect Fan Cables for Damage: Look for frayed wires, bent pins, or broken connectors.
Pro Tip: Use a known working fan to test the CPU_FAN header if you’re unsure.
3. BIOS Configuration Fixes
If the hardware is functional, your BIOS may need adjusting.
- Reset BIOS to Default Settings: Enter BIOS/UEFI and use the “Load Optimized Defaults” option to revert to factory safe configurations.
- Check Fan Monitoring Settings: Enable CPU Fan Control, or adjust the minimum RPM threshold if your fan is too quiet to be detected.
- Update BIOS Firmware: Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest BIOS version. Outdated firmware can cause false fan detection errors.
⚠️ Warning: Always follow manufacturer instructions carefully when updating the BIOS to avoid system instability.
Fan speed errors could be a sign your CPU is overheating.
👉 Learn what temperatures are too hot and how to cool things down in our guide: How Hot Is Too Hot for a CPU? Safe Temps & Cooling.
4. Replacing the CPU Fan
If the fan is non-functional or the error persists, replacement might be necessary.
- Identify Compatible Fans: Match the new fan with your CPU socket type (e.g., Intel LGA 1200, AMD AM4) and ensure the correct power connector (3 pin or 4 pin PWM).
- Install the New Fan Properly:
- Remove the old fan and clean off old thermal paste.
- Apply new thermal paste to the CPU.
- Secure the new fan per manufacturer instructions, ensuring proper pressure and alignment.
- Reconnect it to the correct header and test the system.
Pro Tip: Consider upgrading to a higher performance cooler if you’re also experiencing high CPU temperatures.
Preventive Measures: Avoid CPU Fan Speed Detection Errors
Preventing CPU fan issues is far easier and cheaper than dealing with them after failure. This section outlines practical strategies to maintain system health and avoid future detection errors.
Regular Maintenance
Routine care extends the life of your hardware and reduces the risk of thermal problems.
- Create a Cleaning Schedule: Set reminders to clean your PC every 3 to 6 months, depending on your environment (more often for dusty or pet friendly homes).
- Use Proper Tools: Clean using compressed air and antistatic brushes to avoid damaging components.
- Inspect Cable Management: Keep wires tidy and away from fans to ensure unrestricted airflow.
Pro Tip: Cleaning your PC regularly also improves airflow, reducing heat buildup.
Monitoring Tools for Early Detection
Prevent problems before they happen by keeping an eye on system health in real time.
- Install Monitoring Software: Tools like HWMonitor, SpeedFan, Open Hardware Monitor, or NZXT CAM offer temperature and fan RPM tracking.
- Enable Alerts: Most of these tools let you set up warnings for high temperatures or low fan speeds giving you time to react before serious issues occur.
- Review Logs: Check fan speed trends over time to identify gradual degradation before it leads to failure.
Why it matters: Real time data helps you detect failing fans or blocked vents early.
Optimize System Configuration
Your case layout and system settings can dramatically impact fan performance.
- Improve Airflow: Use a case with well placed intake and exhaust fans, avoid crowding internal components, and position your PC in a well ventilated space.
- Avoid Unnecessary Overclocking: If you’re not using high end cooling, overclocking can push your fan system beyond its limits.
- Match Cooling to Performance Needs: Choose air or liquid cooling depending on usage gamers, streamers, and content creators often benefit from aftermarket cooling solutions.
Tip: Use “positive pressure” airflow configurations to minimize dust intake while improving cooling.
Recommended Solutions from the Community
1. Verify Fan Connections
- Ensure the CPU fan is connected to the correct CPU FAN header.
- If using an AIO cooler, connect the pump’s RPM wire to the CPU FAN header to provide the necessary feedback.
2. Adjust BIOS Settings
- Access the BIOS and navigate to the fan monitoring section.
- Set the CPU fan speed monitoring to “Ignore” or adjust the low RPM threshold to accommodate quieter fans.
3. Update BIOS Firmware
- Ensure your motherboard’s BIOS is up to date, as newer versions may address fan detection issues.
4. Check for Hardware Issues
- Inspect the fan for any physical damage or obstructions.
- Test the fan on another system or header to confirm it’s functioning correctly.
User Experiences & Insights
- Reddit User: A user reported that after a sudden system restart, they began receiving the CPU fan speed detection error, despite the fan spinning and temperatures remaining normal. They resolved the issue by checking BIOS settings and ensuring proper fan connections.
- Tom’s Hardware Forum: A discussion highlighted that even with the fan spinning and temperatures normal, the error persisted until BIOS settings were adjusted to ignore the low RPM threshold.
- ASUS ROG Forum: Users with AIO coolers connected to the AIO PUMP header experienced detection errors, which were resolved by connecting the pump’s RPM wire to the CPU FAN header or adjusting BIOS settings.
Best Practices
- Ensure Proper Connections: Always connect the CPU fan or AIO pump’s RPM wire to the CPU FAN header.
- Adjust BIOS Settings: Modify fan speed monitoring settings to accommodate your cooling solution.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your system clean and check for any obstructions or damage to the fan.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your BIOS to benefit from fixes and improvements.
Real World Applications and Case Studies
Gamer’s Experience with Overheating
Case Study: Mid Game Meltdown Turns Into a Learning Opportunity
Scenario:
A PC gamer reported sudden shutdowns and a persistent “CPU fan speed error” every time they booted their system right in the middle of an intense online session of Call of Duty: Warzone.
Symptoms:
- Loud fan noise before shutdown.
- Error message on BIOS boot screen.
- System logs showing CPU temps exceeding 90°C.
Resolution Steps Taken:
- Immediate Action: Opened the PC case and found thick layers of dust on the CPU fan and heatsink.
- Cleaning: Used compressed air to remove dust and reseated the fan properly.
- Software Monitoring: Installed HWMonitor to track fan RPM and temperatures.
- Replacement: Realized the fan had inconsistent RPM readings and replaced it with a Noctua high performance cooler.
- BIOS Tweaks: Adjusted the fan speed warning threshold in the BIOS to avoid false positives from low RPM modes.
Result:
The error no longer appeared, and system temps stayed under 70°C during peak gaming sessions. The gamer also learned the importance of quarterly cleaning and using monitoring tools.
IT Professional’s Approach to Thermal Management
Insights from the Enterprise Field
Interview Snippet: John M., Systems Administrator at a Managed IT Services Firm
“We manage over 300 desktops and servers, and CPU fan speed errors are common especially in environments where hardware isn’t cleaned regularly or users tinker with BIOS settings.”
Best Practices from the Field:
- Preventive Maintenance Plans:
- Biannual hardware cleanups.
- Scheduled thermal paste replacement every 18 to 24 months.
- Dust filters on all intake fans.
- Enterprise Grade Monitoring:
- Use of Open Hardware Monitor and Paessler PRTG to remotely track CPU temps and fan speeds.
- Set alerts for CPU temps above 80°C or RPMs falling below thresholds.
- Standardized BIOS Policies:
- Company wide policies to prevent end users from modifying BIOS fan settings.
- Centralized BIOS configuration using scripts or management software.
- Cooling Redundancy for Critical Systems:
- Dual fan setups and liquid cooling in high performance workstations.
- Redundant fans in rack mounted servers to ensure uptime.
Pro Insight:
“A single overlooked fan header or dusty fan can spiral into a major ticket if left unchecked. Prevention is cheaper than hardware replacements.”
Common Queries & Solutions for CPU Fan Speed Detection Error
CPU Fan Speed Detection Error on Reddit: What Are Users Saying?
Many users report:
- Fans spinning but motherboard not detecting RPM.
- Issues often stem from BIOS updates or incorrect fan header connections.
- Solutions include BIOS tweaks, fan cable checks, or fan replacement.
- Some report AIO coolers causing false errors due to missing RPM signal.
CPU Fan Speed Detection Error with AIO Coolers
AIO coolers often connect pumps to AIO PUMP headers, which don’t send RPM signals to the CPU FAN header causing errors. To fix:
- Connect the pump’s RPM cable to the CPU FAN header.
- Alternatively, disable CPU fan speed monitoring in BIOS.
- Consult your AIO cooler manual for recommended connections.
Fixing CPU Fan Speed Detection Error on ASUS Motherboards
ASUS motherboards may show this error if:
- The fan is not connected to the CPU FAN header.
- BIOS fan control settings require adjustment.
ASUS Specific Tips:
- Use AI Suite software to monitor fan speeds in Windows.
- In BIOS, disable “CPU Fan Speed Monitor” temporarily if you confirm the fan is working.
- Update to the latest BIOS version from ASUS support site.
How to Ignore CPU Fan Speed Detection Error
In BIOS settings, you can:
- Disable CPU fan speed monitoring.
- Increase the minimum fan speed threshold.
Note: Ignoring this warning risks overheating if the fan actually fails.
Common Error: “Please Ensure Your CPU Cooler is Properly Connected”
This message means the motherboard cannot detect the fan spinning or its RPM. To resolve:
- Double check fan connection to CPU FAN header.
- Inspect fan for physical damage.
- Verify BIOS settings or reset BIOS to defaults.
Fixing CPU Fan Speed Detection Error on Windows 10
The error is BIOS level and usually occurs during POST, but you can monitor fans in Windows:
- Use HWMonitor, SpeedFan, or Core Temp to check fan speeds and temperatures.
- If fan speeds show zero, troubleshoot hardware or BIOS.
CPU Fan Speed Detection Error After BIOS Update
BIOS updates can reset fan control settings causing errors:
- Enter BIOS after update and check fan monitoring settings.
- Reset BIOS to default or reconfigure fan speed thresholds.
- Reflash BIOS if necessary or update to a newer version.
CPU Fan Speed Detection Error on AMI BIOS
AMI BIOS users commonly see this error if:
- Fan is disconnected or faulty.
- BIOS fan monitoring thresholds are too strict.
Solutions:
- Enter BIOS → Advanced → Hardware Monitor.
- Adjust or disable fan speed alarms temporarily.
- Check connections and fan health.
Why Do I See the CPU FAN Error in POST?
POST (Power On Self Test) checks CPU fan RPM. The error appears if:
- CPU fan isn’t detected or spinning fast enough.
- Fan header is wrong or cable is loose.
- Fan is defective or fan speed is below BIOS threshold.
2 Ways to Fix the CPU Fan Speed Detection Error
Method 1: Hardware Check and Maintenance
- Check fan connections and cables.
- Clean dust from fans and heatsinks.
- Replace faulty fans.
Method 2: BIOS Configuration
- Reset BIOS to default.
- Disable or ignore CPU fan speed warnings (temporarily).
- Update BIOS firmware.
Conclusion
The CPU fan speed detection error is a critical warning that shouldn’t be ignored. Regular maintenance, proper BIOS configuration, and prompt troubleshooting can prevent and resolve this issue.
Don’t let a simple error compromise your system’s health. Follow our comprehensive guide to ensure your CPU stays cool and your PC runs efficiently.